Across India-
Across Asia
Across Pacific & Asia
Across Pacific & Asia
Communications:
------------------------------------------------------------
|
| .......................................................................... |
.. |
...........................
.............................................................. .................
|
| ........ |
..............................Building Bridges ACROSS the Barriers.................................... .............................................................................. |
........ |

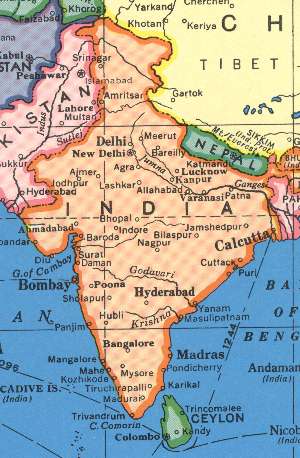 smaller Muslim state of Pakistan. In
1971 a
third war
between the two
smaller Muslim state of Pakistan. In
1971 a
third war
between the two  countries resulted
in East Pakistan becoming
the separate nation of Bangladesh. Major concerns in India
include the ongoing dispute with Pakistan over Kashmir, massive
overpopulation, environmental degradation, extensive poverty, and
ethnic and religious strife. Yet India has impressive gains in
economic investment and output.
countries resulted
in East Pakistan becoming
the separate nation of Bangladesh. Major concerns in India
include the ongoing dispute with Pakistan over Kashmir, massive
overpopulation, environmental degradation, extensive poverty, and
ethnic and religious strife. Yet India has impressive gains in
economic investment and output.