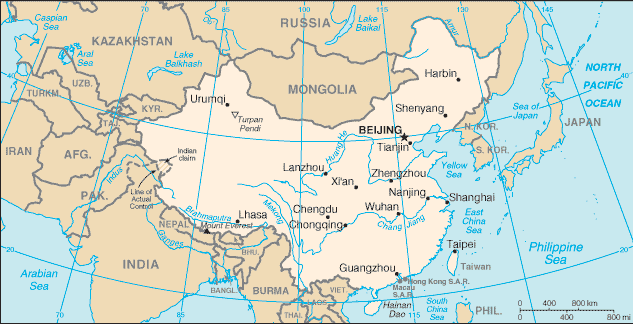
Across China-
Across Asia
Across Pacific & Asia
Across Pacific & Asia
Primary Source: World Fact Book
|
| .......................................................................... |
.. |
...........................
Across Asia...... .................
|
| ........ |
..............................Building Bridges ACROSS the Barriers.................................... .............................................................................. |
........ |